Recently Google had announced that:
Google uses structured data standardized formats and shared schemas to provide information about a page and the things described by the page. This information is used for two main purposes:
- Understand the content of the page
- Enable special search result features and enhancements
Yesterday Google has announced:
We support review snippets in Google Search Console, and include new reports to help you find any issues with your implementation and monitor how this rich result type is improving your performance. You can also use the Rich Results Test to review your existing URLs or debug your markup code before moving it to production.
This is a clear indication that Google is giving more and more importance to Structured Data for various aspects.
Here Google clearly states that :
To help site owners make the most of their reviews, a new review snippet report is now available in Search Console for sites that have implemented reviews or ratings structured data. The report allows you to see errors, warnings, and valid pages for markup implemented on your site.
The Performance report shows the Review Snippet Results
The Search Console Performance report now allows you to see the performance of your review or rating marked-up pages on Google Search and Discover using the new “Review snippet” search appearance filter.
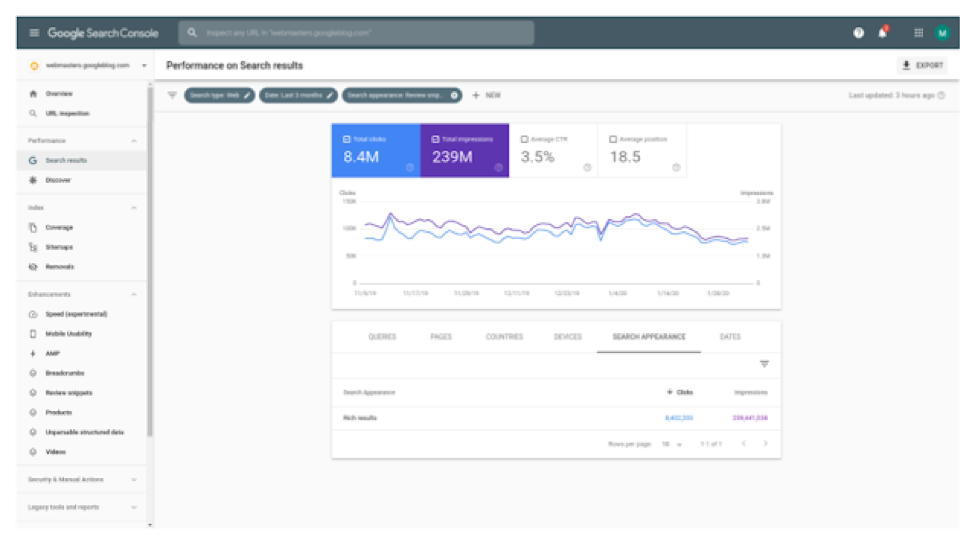
This helps you filter your data to see which queries, pages, countries and devices are bringing your review snippets traffic.
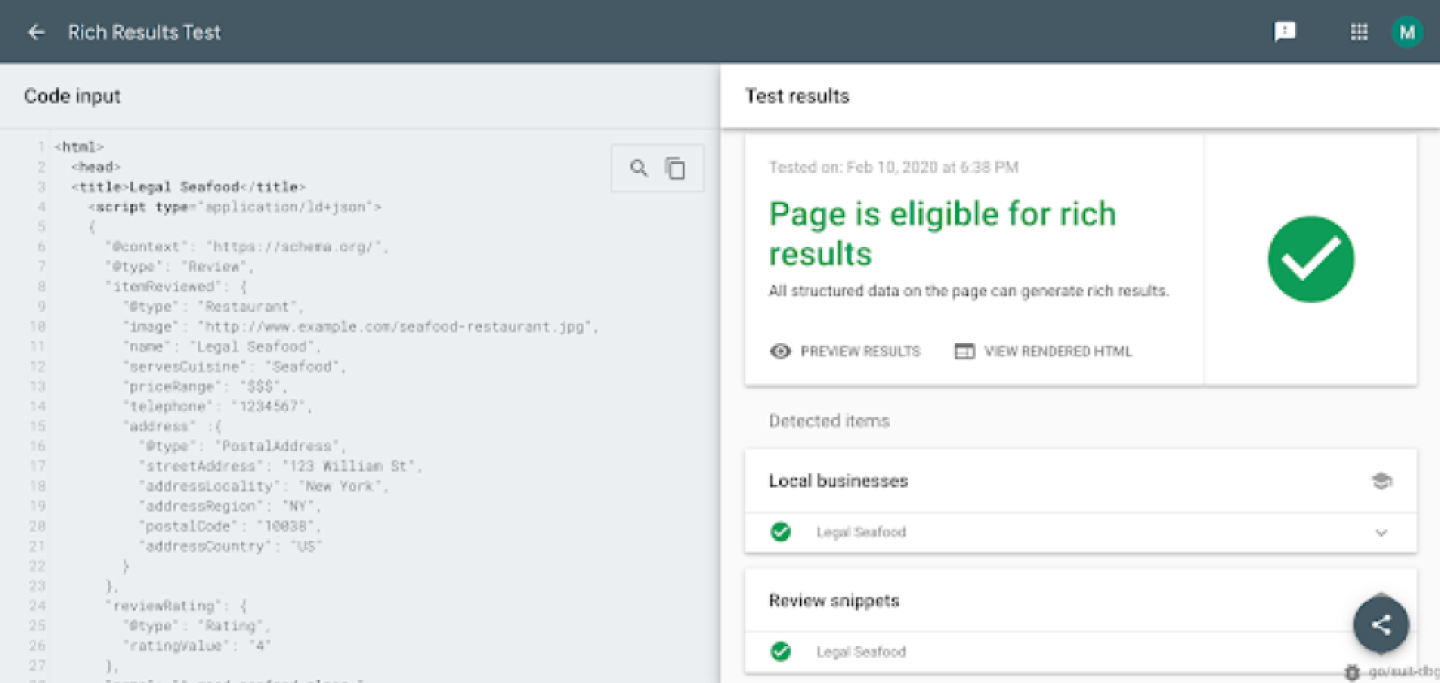
Review snippet in Rich Results Test
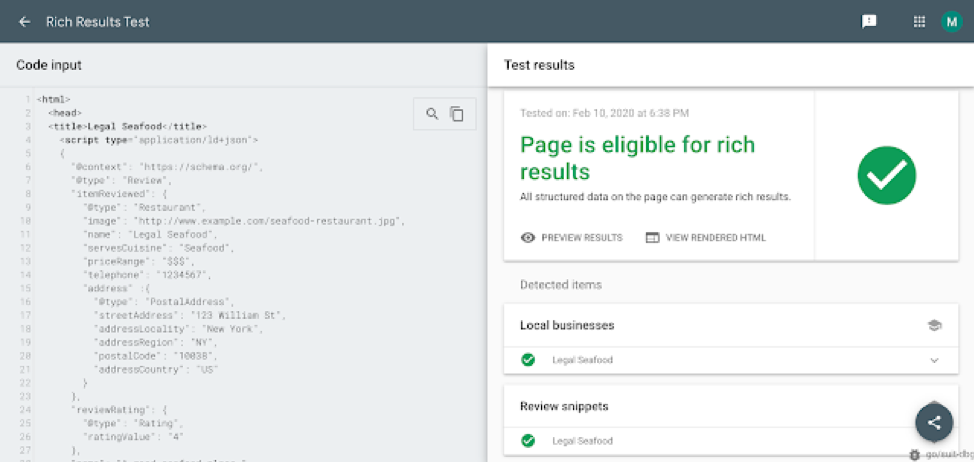
After adding Review snippets structured data to your pages, you can test them using the Rich Results Test tool. You can test a code snippet or submit a URL of a page.

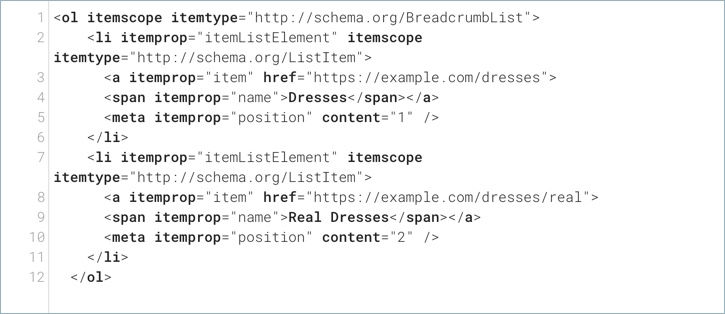

.png)









