What Is Voice Search
Voice search uses speech recognition technology. The users ask their queries and search information through voice instead of typing it.
Google Voice Search or Search by Voice is a Google product that allows users to use Google Search by speaking on a mobile phone or computer, i.e. have the device search for data upon entering information on what to search into the device by speaking.
Typed search queries and voice search queries are worded differently even if the person has the same search intent.
For example: In a text search, you would probably type “best Chinese restaurants in Mumbai;” but if you were to do a voice search, you would be more likely to ask, “is there any good Chinese food around here?”
A voice search is more conversational in style.
When the user uses text search, it is a brief phrase that he keys in. In voice search the user starts a conversation with the device which is a proper question or a sentence.
Hence, more that keywords it is the intent of the search query which is assessed before the search results are served to the user.
Devices Used For Voice Search
- There are different voice search devices are available in the market
- Amazon Echo/Alexa.
- Siri/iPhone.
- Google Home.
- Microsoft Cortana.
- Google Assistant.
- Android Phones.
- Tablets (iPad and Android)
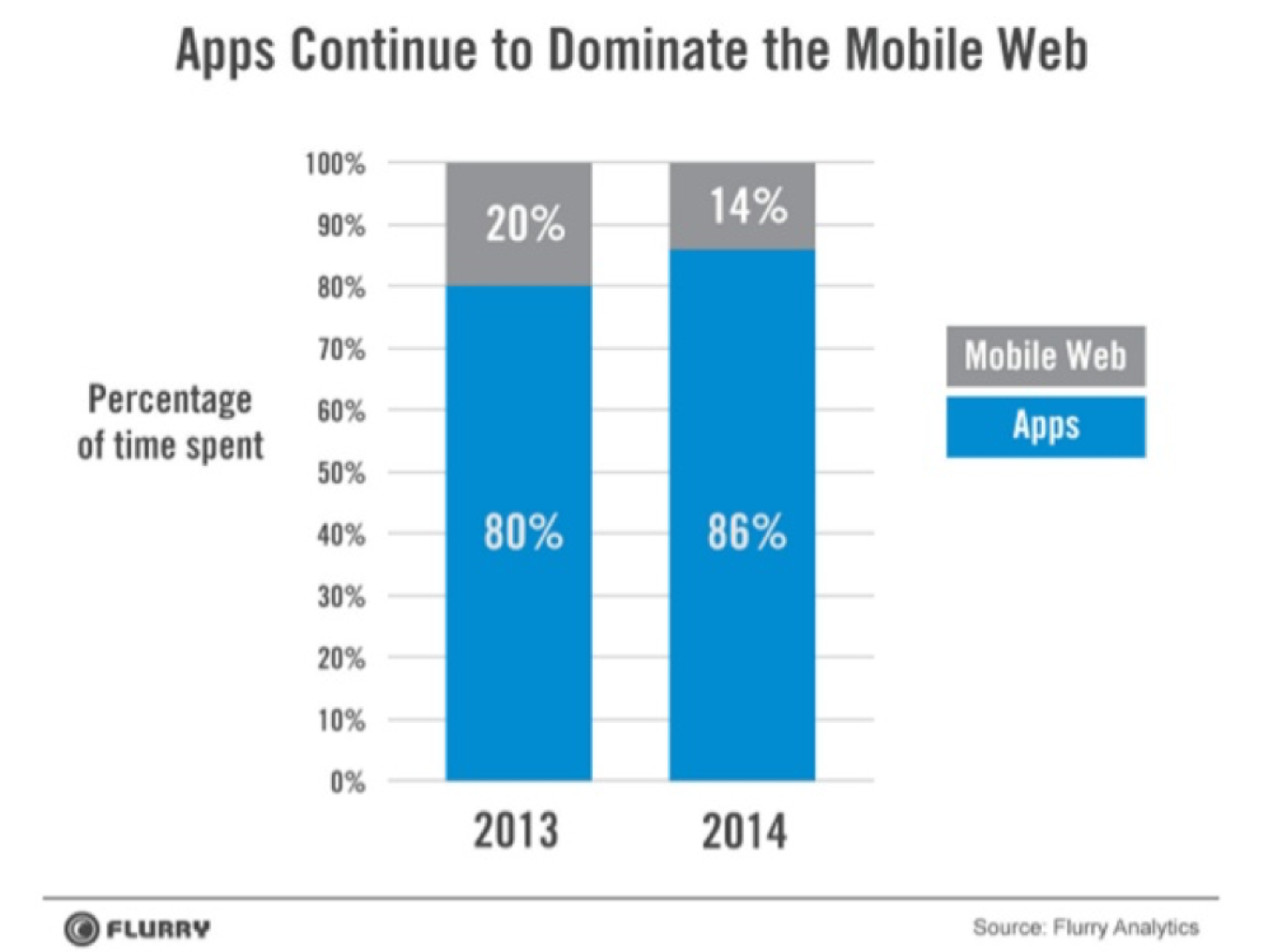
The Increasing use of Voice Search (Some Stats.)

Types Of Voice Search Queries :
Voice search queries as of now can be categorized in the above 4 categories.

I want to know moments
I want to go moments

I want to do moments

I want to buy moments

How To Optimize for Voice Search
The focus for voice search is basically the searcher intent rather than the keywords. But, that does not mean that the basic on-page can be given a skip. The on-page and Technical factors will continue to be important.
In addition to the on-page and technical factors the priority needs to be given to the following:
- Try to rank for :
* Featured snippets
*Local Search Results
*Long tail search queries
2.Implement Schemas
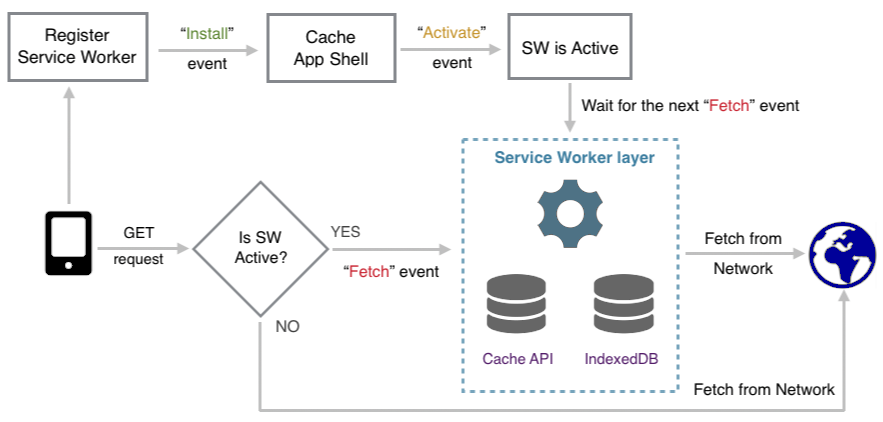
3.Make Mobile Optimization a priority (Read More about Mobile Friendliness in our previous post https://www.webpro.in/what-does-it-mean-to-have-a-mobile-ready-website-in-2018-with-an-emphasis-on-pwa-progressive-web-apps/)