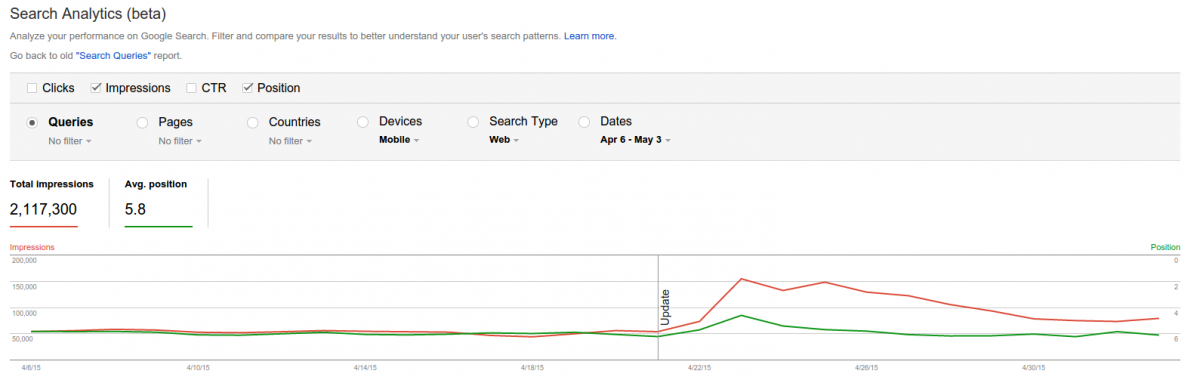
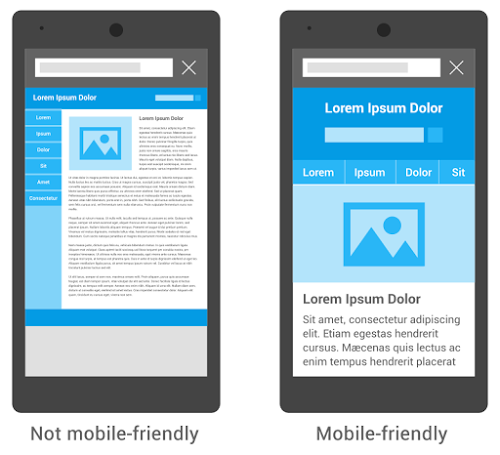
Google announced recently that RankBrain is Google’s name for a machine-learning artificial intelligence system that’s used to help process its search results. They also added that RankBrain is one of the “hundreds” of signals that go into an algorithm that determines what results appear on a Google search page and where they are ranked. In the few months it has been deployed, RankBrain has become the third-most important signal contributing to the result of a search query. We have been also recently been talking about the semantic web .In one of our previous blog posts http://www.webpro.in/how-the-semantic-web-html5-microformats-and-seo-are-inter-linked/ the 4 quadrants which explain the information and social connectivity very effectively have the semantic web and artificial intelligence in the same quadrant. The semantic web connects knowledge.
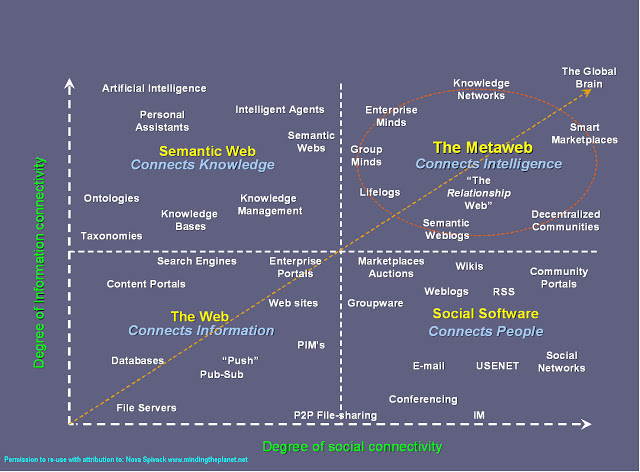
Semantics is about "real objects and imaginary concepts and the particular relations between them!" (cf. Berners-Lee 94) And the field that knows how to do this is AI (Artificial Intelligence)! (We call it "knowledge representation"!) According to James Hendler in one of his presentation about the semantic web he says: knowledge representation … is currently in a state comparable to that of hypertext before the advent of the web: it is clearly a good idea, and some very nice demonstrations exist, but it has not yet changed the world. It contains the seeds of important applications, but to unleash its full power it must be linked into a single global system. -- Berners-Lee, Hendler, Lassila, 2001. RankBrain the machine-learning artificial intelligence system is a software which is integrated into the algorithm to mathematically connect words and phrases. An interesting paper on Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality explains the way words and phrases can be mathematically connected. In this paper Google has mentioned :
- Distributed representations of words in a vector space help learning algorithms to achieve better performance in natural language processing tasks by grouping similar words
- Word representations are limited by their inability to represent idiomatic phrases that are not compositions of the individual words. For example, “Boston Globe” is a newspaper, and so it is not a natural combination of the meanings of “Boston” and “Globe”
- Other techniques that aim to represent meaning of sentences by composing the word vectors, such as the recursive autoencoders , would also benefit from using phrase vectors instead of the word vectors.
- The extension from word based to phrase based models is relatively simple. First we identify a large number of phrases using a data-driven approach, and then we treat the phrases as individual tokens during the training. To evaluate the quality of the phrase vectors, we developed a test set of analogical reasoning tasks that contains both words and phrases. A typical analogy pair from our test set is “Montreal”:“Montreal Canadiens”::“Toronto”:“Toronto Maple Leafs”. It is considered to have been answered correctly if the nearest representation to vec(“Montreal Canadiens”) - vec(“Montreal”) + vec(“Toronto”) is vec(“Toronto Maple Leafs”). We found that simple vector addition can often produce meaningful results. For example, vec(“Russia”) + vec(“river”) is close to vec(“Volga River”), and vec(“Germany”) + vec(“capital”) is close to vec(“Berlin”). This compositionality suggests that a non-obvious degree of language understanding can be obtained by using basic mathematical operations on the word vector representations.
- A very interesting result of this work is that the word vectors can be somewhat meaningfully combined using just simple vector addition. Another approach for learning representations of phrases presented in this paper is to simply represent the phrases with a single token. Combination of these two approaches gives a powerful yet simple way how to represent longer pieces of text, while having minimal computational complexity. Our work can thus be seen as complementary to the existing approach that attempts to represent phrases using recursive matrix-vector operations .
According to Google's senior research scientist Greg Corrado Once RankBrain analyzes the text through vectors, it can isolate words or phrases it doesn't understand. It can then guess the meaning based on similar words and phrases and filter the results accordingly. When a search takes place on Google, the search query now will be accessed by the RankBrain program/software to deliver more relevant search results. Especially if the query is a rare one. By making the query accessible to software (RankBrain), the software will essentially become able to understand knowledge, think about knowledge via mathematical computations using word and phrase vectors, and create new knowledge. In other words, software will be able to be more intelligent – not as intelligent as humans perhaps, but more intelligent than say, the word to word mapping is today. Especially for rare queries which need to be understood to deliver results. As Semantics adds extra information to help you with the meaning of the information. Websites using Schemas will be able to get more correlated to the contextual content.
Why schemas will become increasingly important from the SEO perspective?
The Semantic Web does not only exist on Web pages.Web 3.0 works inside of applications and databases, not just on Web pages. Calling it a “Web” is a misnomer of sorts — it’s not just about the Web, it’s about all information, data and applications. More information on http://www.w3.org/DesignIssues/LinkedData.html As the data on the web goes on expanding and the snowball of data gradually becoming an avalanche , as James Hendler says, a little semantic will go a long way.
The Semantic Web isn't just about putting data on the web. It is about making links, so that a person or machine can explore the web of data. With linked data, when you have some of it, you can find other, related, data.
In the video below James Hendler mentions that Mr. Guha who started Schema.org said that Google uses the RDF/Microformats and he mentioned at the WWW conference that 20% (5 million domains) have schemas on it (Video 41:48). He says in 2001 Google had said that they would not be using schemas in a big way but now they have integrated it in the search algorithm. The knowledge graph is one such example. Google Turning Its Lucrative Web Search Over to AI Machines (Bloomberg Video) // In this new quality era of search we have to move our focus away from keywords and focus more on the keyness factor of the content which has the potential to correlate to searches made on the search engines as the semantic web adds more meaning to the query for a search rather than just mapping words during the search process. (Note: I know there is no such word as "keyness" but by the "keyness factor" I mean the the correlation, relevance, and the essence of the content rather than the actual word to word keyword mapping.)
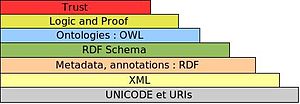
As you can see in the image above, we have URI and Unicode as the basis of the web. This can be called the first step which adds the keyness to the webpage and the content of that page that you want to promote organically on search engines or on the web. The keyness factor can be derived from the context of the terms, terminolgy and text used in the content of URl, title, headings, anchor text of the inbound links, alt text used on images, schema codes, meta tags, microformats and body text. If we focus on the keyness factor and try to cater to correlate to a wide range of keyword data rather than focusing on the keywords alone in the URLs, titles and descriptions it gets passed on to the next layer of the emerging web, making the pages pass on more correlation and relevance and also syncs the on page signals with the off-page signals which get directly indexed in the search engines in the form of feeds and sitemaps. More about keyness, Semantic Web and correlation on http://searchenginewatch.com/sew/opinion/2214849/googles-knowledge-graph-implications-for-search-seo Of course the web today is also about mobility, security and interaction (Social Media) but as an SEO I think representing content in the form of structured data as much as possible will surely be one of the ways to future proof the search presence of any website as datasets of any schema surely add meaning to the content for any crawler in the form of the meaningful records and fields.